Bulgarian - Wikilangs Models
Comprehensive Research Report & Full Ablation Study
This repository contains NLP models trained and evaluated by Wikilangs, specifically on Bulgarian Wikipedia data. We analyze tokenizers, n-gram models, Markov chains, vocabulary statistics, and word embeddings.
📋 Repository Contents
Models & Assets
- Tokenizers (8k, 16k, 32k, 64k)
- N-gram models (2, 3, 4, 5-gram)
- Markov chains (context of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5)
- Subword N-gram and Markov chains
- Embeddings in various sizes and dimensions (aligned and unaligned)
- Language Vocabulary
- Language Statistics
Analysis and Evaluation
- 1. Tokenizer Evaluation
- 2. N-gram Model Evaluation
- 3. Markov Chain Evaluation
- 4. Vocabulary Analysis
- 5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
- 6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
- 7. Summary & Recommendations
- Metrics Glossary
- Visualizations Index
1. Tokenizer Evaluation
Results
| Vocab Size | Compression | Avg Token Len | UNK Rate | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
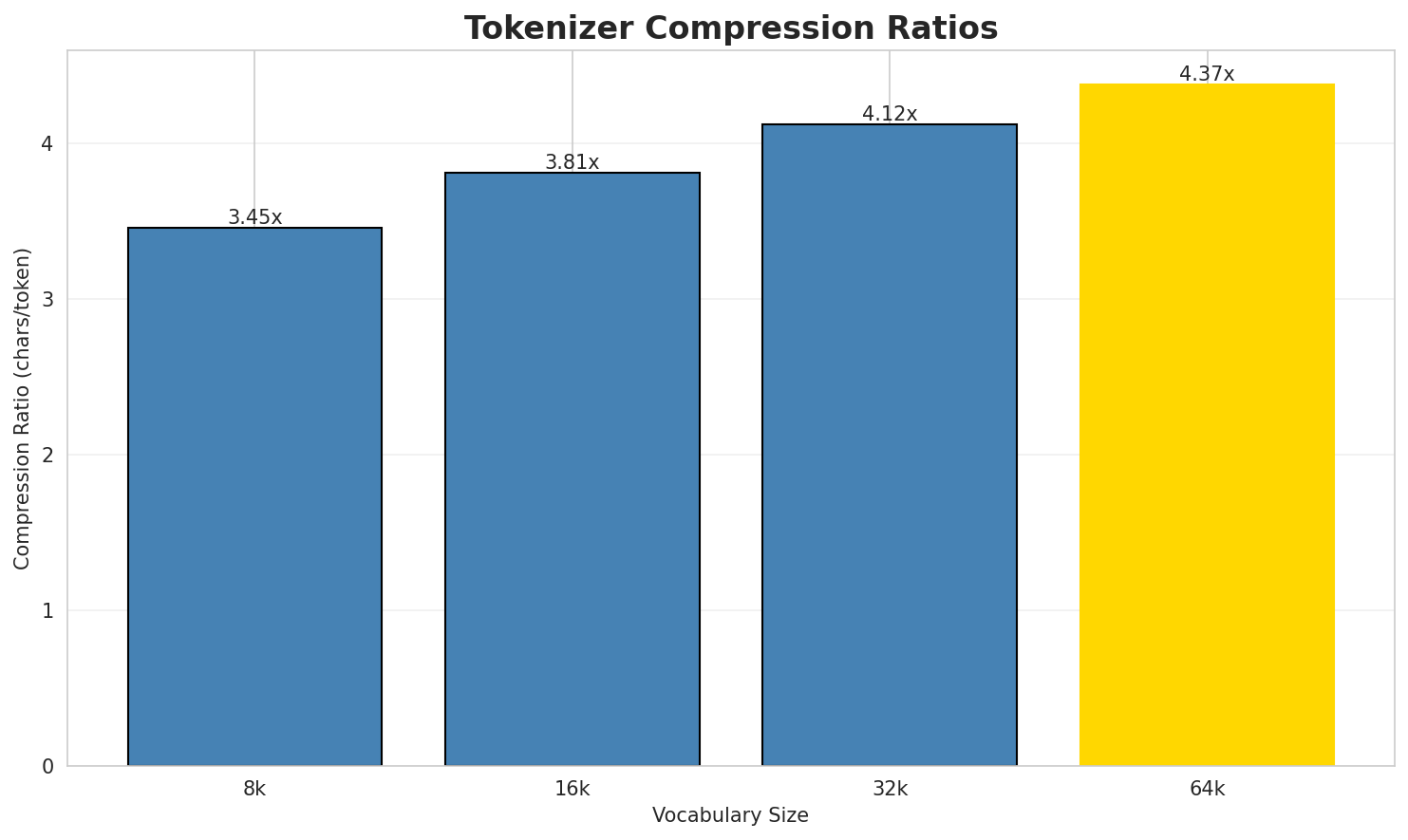
| 8k | 3.452x | 3.45 | 0.0493% | 2,552,470 |
| 16k | 3.809x | 3.81 | 0.0544% | 2,313,214 |
| 32k | 4.120x | 4.12 | 0.0589% | 2,138,945 |
| 64k | 4.373x 🏆 | 4.37 | 0.0625% | 2,015,292 |
Tokenization Examples
Below are sample sentences tokenized with each vocabulary size:
Sample 1: Часово отместване UTC-11 се използва в: : Американска Самоа, Атол Мидуей : Ниуе ...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁ча сово ▁от мест ване ▁utc - 1 1 ▁се ... (+17 more) |
27 |
| 16k | ▁ча сово ▁от мест ване ▁utc - 1 1 ▁се ... (+15 more) |
25 |
| 32k | ▁ча сово ▁от местване ▁utc - 1 1 ▁се ▁използва ... (+13 more) |
23 |
| 64k | ▁часово ▁отместване ▁utc - 1 1 ▁се ▁използва ▁в : ... (+9 more) |
19 |
Sample 2: Synodontis ouemeensis е вид лъчеперка от семейство Mochokidae. Разпространение В...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁s yn od ont is ▁o u em e ensis ... (+22 more) |
32 |
| 16k | ▁syn odont is ▁o u em e ensis ▁е ▁вид ... (+20 more) |
30 |
| 32k | ▁syn odont is ▁ou em e ensis ▁е ▁вид ▁лъчеперка ... (+19 more) |
29 |
| 64k | ▁synodontis ▁ou eme ensis ▁е ▁вид ▁лъчеперка ▁от ▁семейство ▁mochokidae ... (+13 more) |
23 |
Sample 3: Orthotomus derbianus е вид птица от семейство Cisticolidae. Разпространение Видъ...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁or th ot om us ▁der b ian us ▁е ... (+22 more) |
32 |
| 16k | ▁or th ot omus ▁der b ianus ▁е ▁вид ▁птица ... (+17 more) |
27 |
| 32k | ▁orth ot omus ▁der b ianus ▁е ▁вид ▁птица ▁от ... (+14 more) |
24 |
| 64k | ▁orth ot omus ▁der b ianus ▁е ▁вид ▁птица ▁от ... (+13 more) |
23 |
Key Findings
- Best Compression: 64k achieves 4.373x compression
- Lowest UNK Rate: 8k with 0.0493% unknown tokens
- Trade-off: Larger vocabularies improve compression but increase model size
- Recommendation: 32k vocabulary provides optimal balance for production use
2. N-gram Model Evaluation
Results
| N-gram | Variant | Perplexity | Entropy | Unique N-grams | Top-100 Coverage | Top-1000 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-gram | Word | 246,747 | 17.91 | 2,004,902 | 5.8% | 16.2% |
| 2-gram | Subword | 385 🏆 | 8.59 | 20,810 | 61.1% | 97.4% |
| 3-gram | Word | 1,033,483 | 19.98 | 4,251,847 | 2.5% | 8.2% |
| 3-gram | Subword | 3,528 | 11.78 | 189,319 | 23.2% | 62.6% |
| 4-gram | Word | 2,692,464 | 21.36 | 7,308,829 | 1.5% | 5.1% |
| 4-gram | Subword | 21,676 | 14.40 | 1,191,303 | 10.4% | 32.6% |
| 5-gram | Word | 2,278,792 | 21.12 | 5,264,454 | 1.8% | 5.4% |
| 5-gram | Subword | 93,842 | 16.52 | 4,256,227 | 5.4% | 19.0% |
Top 5 N-grams by Size
2-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | през г |
371,674 |
| 2 | да се |
178,835 |
| 3 | през година |
109,499 |
| 4 | външни препратки |
108,119 |
| 5 | е на |
90,144 |
3-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | по време на |
72,585 |
| 2 | източници външни препратки |
52,888 |
| 3 | пр н е |
38,682 |
| 4 | може да се |
32,598 |
| 5 | през г е |
28,945 |
4-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | разпространение видът е разпространен |
11,928 |
| 2 | видът е разпространен в |
11,811 |
| 3 | може да се отнася |
9,394 |
| 4 | външни препратки официален сайт |
9,248 |
| 5 | застрашен от изчезване разпространение |
9,061 |
5-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | разпространение видът е разпространен в |
11,030 |
| 2 | може да се отнася за |
8,323 |
| 3 | е вид птица от семейство |
8,165 |
| 4 | източници външни препратки уебсайт на |
7,757 |
| 5 | външни препратки уебсайт на общината |
7,230 |
2-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | а _ |
22,221,689 |
| 2 | н а |
13,044,169 |
| 3 | и _ |
12,174,707 |
| 4 | _ с |
10,248,868 |
| 5 | _ н |
9,602,446 |
3-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | н а _ |
8,421,175 |
| 2 | _ н а |
7,714,836 |
| 3 | _ п р |
3,824,613 |
| 4 | т а _ |
3,691,871 |
| 5 | т о _ |
3,556,816 |
4-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ н а _ |
5,969,377 |
| 2 | а т а _ |
2,454,178 |
| 3 | _ о т _ |
2,129,103 |
| 4 | а _ н а |
1,914,071 |
| 5 | _ п р е |
1,889,917 |
5-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | а _ н а _ |
1,515,525 |
| 2 | е _ н а _ |
949,109 |
| 3 | _ п р е з |
882,206 |
| 4 | п р е з _ |
849,611 |
| 5 | о _ н а _ |
755,344 |
Key Findings
- Best Perplexity: 2-gram (subword) with 385
- Entropy Trend: Decreases with larger n-grams (more predictable)
- Coverage: Top-1000 patterns cover ~19% of corpus
- Recommendation: 4-gram or 5-gram for best predictive performance
3. Markov Chain Evaluation
Results
| Context | Variant | Avg Entropy | Perplexity | Branching Factor | Unique Contexts | Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Word | 0.9743 | 1.965 | 12.25 | 1,896,771 | 2.6% |
| 1 | Subword | 1.0920 | 2.132 | 7.98 | 9,126 | 0.0% |
| 2 | Word | 0.3814 | 1.303 | 2.47 | 23,216,480 | 61.9% |
| 2 | Subword | 0.7778 | 1.714 | 5.53 | 72,830 | 22.2% |
| 3 | Word | 0.1657 | 1.122 | 1.39 | 57,272,367 | 83.4% |
| 3 | Subword | 0.8207 | 1.766 | 4.91 | 403,072 | 17.9% |
| 4 | Word | 0.0723 🏆 | 1.051 | 1.13 | 79,394,777 | 92.8% |
| 4 | Subword | 0.7498 | 1.682 | 3.81 | 1,979,446 | 25.0% |
Generated Text Samples (Word-based)
Below are text samples generated from each word-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
на излезли преди тази система от общинския център е най доброто от контекстовото запитване за написв...в миналото корабите от своето поведение и актриси актьори рок група в колекциониране на военноморска...и денчевци и е посрещала годеницата на черноморец бургас община палеор φούφας антиполохагос атина за...
Context Size 2:
през г тъй като години българия медал за на барила през г в битката е част отда се шуми около връзката ѝ с република българия собствеността на международна научна конференция га...външни препратки официален сайт схема на телескопа е било напълно елиминирано съмнението на ръководс...
Context Size 3:
по време на празничния сезон и стачката в метрото в токио vx не се използва от национално музикалноизточници външни препратки официален сайт на метеор първите ѝ постановки са дипломният ѝ спектакъл с...пр н е и са изключително популярни на балканите и втората най обща сред мъжете по онова време
Context Size 4:
разпространение видът е разпространен в малави мозамбик и j placidochromis johnstoni in iucn iucn re...видът е разпространен в демократична република t lamprologus lethops in iucn iucn red list of threat...може да се отнася до фердинандо i де медичи за да приюти извънбрачните дъщери на алесандро за разлик...
Generated Text Samples (Subword-based)
Below are text samples generated from each subword-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
_трхтвътва_бъно_а_ma_верг._п_ц_мита_менизандиясн
Context Size 2:
а_преват_и_с_ко_кна_сед_хеърши_ак:и_от_стори_те_съе
Context Size 3:
на_кампийский_став_на_от_вите_ръчепе_прически_баваща_с
Context Size 4:
_на_шаламброзиеологата_е_важна_космиче_от_попов_конвойна_
Key Findings
- Best Predictability: Context-4 (word) with 92.8% predictability
- Branching Factor: Decreases with context size (more deterministic)
- Memory Trade-off: Larger contexts require more storage (1,979,446 contexts)
- Recommendation: Context-3 or Context-4 for text generation
4. Vocabulary Analysis
Statistics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary Size | 888,624 |
| Total Tokens | 105,654,230 |
| Mean Frequency | 118.90 |
| Median Frequency | 4 |
| Frequency Std Dev | 9303.24 |
Most Common Words
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | на | 5,995,585 |
| 2 | в | 3,186,690 |
| 3 | и | 3,167,004 |
| 4 | е | 2,175,525 |
| 5 | от | 2,154,986 |
| 6 | за | 1,348,073 |
| 7 | се | 1,261,391 |
| 8 | г | 1,205,312 |
| 9 | с | 1,088,412 |
| 10 | през | 849,597 |
Least Common Words (from vocabulary)
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | кепевци | 2 |
| 2 | сарджовци | 2 |
| 3 | мъндън | 2 |
| 4 | талиевия | 2 |
| 5 | carbonato | 2 |
| 6 | tallio | 2 |
| 7 | разр | 2 |
| 8 | барутхана | 2 |
| 9 | азадлу | 2 |
| 10 | шталаг | 2 |
Zipf's Law Analysis
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zipf Coefficient | 0.9425 |
| R² (Goodness of Fit) | 0.997405 |
| Adherence Quality | excellent |
Coverage Analysis
| Top N Words | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Top 100 | 35.2% |
| Top 1,000 | 53.9% |
| Top 5,000 | 70.2% |
| Top 10,000 | 77.2% |
Key Findings
- Zipf Compliance: R²=0.9974 indicates excellent adherence to Zipf's law
- High Frequency Dominance: Top 100 words cover 35.2% of corpus
- Long Tail: 878,624 words needed for remaining 22.8% coverage
5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
5.1 Cross-Lingual Alignment
5.2 Model Comparison
| Model | Dimension | Isotropy | Semantic Density | Alignment R@1 | Alignment R@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono_32d | 32 | 0.7975 🏆 | 0.3595 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_64d | 64 | 0.7851 | 0.2896 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_128d | 128 | 0.7344 | 0.2334 | N/A | N/A |
| aligned_32d | 32 | 0.7975 | 0.3609 | 0.1560 | 0.5140 |
| aligned_64d | 64 | 0.7851 | 0.2794 | 0.3420 | 0.7340 |
| aligned_128d | 128 | 0.7344 | 0.2326 | 0.4740 | 0.8180 |
Key Findings
- Best Isotropy: mono_32d with 0.7975 (more uniform distribution)
- Semantic Density: Average pairwise similarity of 0.2926. Lower values indicate better semantic separation.
- Alignment Quality: Aligned models achieve up to 47.4% R@1 in cross-lingual retrieval.
- Recommendation: 128d aligned for best cross-lingual performance
6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
This section presents an automated morphological analysis derived from the statistical divergence between word-level and subword-level models. By analyzing where subword predictability spikes and where word-level coverage fails, we can infer linguistic structures without supervised data.
6.1 Productivity & Complexity
| Metric | Value | Interpretation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Productivity Index | 5.000 | High morphological productivity | Reliable analysis |
| Idiomaticity Gap | -0.715 | Low formulaic content | - |
6.2 Affix Inventory (Productive Units)
These are the most productive prefixes and suffixes identified by sampling the vocabulary for global substitutability patterns. A unit is considered an affix if stripping it leaves a valid stem that appears in other contexts.
Productive Prefixes
| Prefix | Examples |
|---|---|
-пр |
предхождащ, прихлупена, правнообвързващи |
Productive Suffixes
| Suffix | Examples |
|---|---|
-а |
исаака, жижавица, гамета |
-та |
гамета, лопатовидната, малинката |
-те |
врапчиште, древноиндийските, регресионните |
-ите |
древноиндийските, регресионните, циментовите |
-ата |
лопатовидната, малинката, покойницата |
-ни |
пълнозначни, шекони, капсулни |
-ки |
весегонски, гаговски, бачовски |
-ия |
шумния, напрежения, валутния |
6.3 Bound Stems (Lexical Roots)
Bound stems are high-frequency subword units that are semantically cohesive but rarely appear as standalone words. These often correspond to the 'core' of a word that requires inflection or derivation to be valid.
| Stem | Cohesion | Substitutability | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
лгар |
2.07x | 163 contexts | елгар, илгар, юлгар |
нска |
1.82x | 254 contexts | анска, энска, юнска |
анск |
1.39x | 921 contexts | данск, анска, банск |
ийск |
1.57x | 389 contexts | бийск, ийски, лийски |
нски |
1.49x | 508 contexts | янски, ански, онски |
ълга |
2.34x | 39 contexts | дълга, бълга, ългаз |
емвр |
2.64x | 21 contexts | ноемвр, декемвр, нпември |
рски |
1.42x | 269 contexts | юрски, врски, ерски |
точн |
1.58x | 134 contexts | точни, точно, точна |
ичес |
1.43x | 204 contexts | бичес, уичес, ическ |
остр |
1.37x | 215 contexts | остри, остро, остра |
ение |
1.49x | 123 contexts | пение, шение, мение |
6.4 Affix Compatibility (Co-occurrence)
This table shows which prefixes and suffixes most frequently co-occur on the same stems, revealing the 'stacking' rules of the language's morphology.
| Prefix | Suffix | Frequency | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
-пр |
-а |
59 words | пріложіха, приложната |
-пр |
-те |
21 words | притеснявайте, профилиращите |
-пр |
-та |
20 words | приложната, притежаващата |
-пр |
-ите |
18 words | профилиращите, пребогатите |
-пр |
-ата |
16 words | приложната, притежаващата |
-пр |
-ия |
15 words | противоракетния, притежания |
-пр |
-то |
13 words | прозводството, препострояването |
-пр |
-ни |
9 words | производни, предхождани |
-пр |
-ки |
7 words | прокарвайки, правейки |
-пр |
-на |
6 words | приблизителна, престъпна |
6.5 Recursive Morpheme Segmentation
Using Recursive Hierarchical Substitutability, we decompose complex words into their constituent morphemes. This approach handles nested affixes (e.g., prefix-prefix-root-suffix).
| Word | Suggested Split | Confidence | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|
| пробитите | пр-обит-ите |
6.0 | обит |
| натрупванията | натрупван-ия-та |
6.0 | натрупван |
| смразяващата | смразяващ-ата |
4.5 | смразяващ |
| лишаването | лишаване-то |
4.5 | лишаване |
| телепатия | телепат-ия |
4.5 | телепат |
| плодородното | плодородно-то |
4.5 | плодородно |
| маловажното | маловажно-то |
4.5 | маловажно |
| стигналите | стигнал-ите |
4.5 | стигнал |
| латинизирани | латинизира-ни |
4.5 | латинизира |
| уругвайското | уругвайско-то |
4.5 | уругвайско |
| паразитология | паразитолог-ия |
4.5 | паразитолог |
| реализираната | реализиран-ата |
4.5 | реализиран |
| изчислимостта | изчислимост-та |
4.5 | изчислимост |
| истинностни | истинност-ни |
4.5 | истинност |
| паратаксалното | паратаксално-то |
4.5 | паратаксално |
6.6 Linguistic Interpretation
Automated Insight: The language Bulgarian shows high morphological productivity. The subword models are significantly more efficient than word models, suggesting a rich system of affixation or compounding.
7. Summary & Recommendations
Production Recommendations
| Component | Recommended | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenizer | 64k BPE | Best compression (4.37x) |
| N-gram | 2-gram | Lowest perplexity (385) |
| Markov | Context-4 | Highest predictability (92.8%) |
| Embeddings | 100d | Balanced semantic capture and isotropy |
Appendix: Metrics Glossary & Interpretation Guide
This section provides definitions, intuitions, and guidance for interpreting the metrics used throughout this report.
Tokenizer Metrics
Compression Ratio
Definition: The ratio of characters to tokens (chars/token). Measures how efficiently the tokenizer represents text.
Intuition: Higher compression means fewer tokens needed to represent the same text, reducing sequence lengths for downstream models. A 3x compression means ~3 characters per token on average.
What to seek: Higher is generally better for efficiency, but extremely high compression may indicate overly aggressive merging that loses morphological information.
Average Token Length (Fertility)
Definition: Mean number of characters per token produced by the tokenizer.
Intuition: Reflects the granularity of tokenization. Longer tokens capture more context but may struggle with rare words; shorter tokens are more flexible but increase sequence length.
What to seek: Balance between 2-5 characters for most languages. Arabic/morphologically-rich languages may benefit from slightly longer tokens.
Unknown Token Rate (OOV Rate)
Definition: Percentage of tokens that map to the unknown/UNK token, indicating words the tokenizer cannot represent.
Intuition: Lower OOV means better vocabulary coverage. High OOV indicates the tokenizer encounters many unseen character sequences.
What to seek: Below 1% is excellent; below 5% is acceptable. BPE tokenizers typically achieve very low OOV due to subword fallback.
N-gram Model Metrics
Perplexity
Definition: Measures how "surprised" the model is by test data. Mathematically: 2^(cross-entropy). Lower values indicate better prediction.
Intuition: If perplexity is 100, the model is as uncertain as if choosing uniformly among 100 options at each step. A perplexity of 10 means effectively choosing among 10 equally likely options.
What to seek: Lower is better. Perplexity decreases with larger n-grams (more context). Values vary widely by language and corpus size.
Entropy
Definition: Average information content (in bits) needed to encode the next token given the context. Related to perplexity: perplexity = 2^entropy.
Intuition: High entropy means high uncertainty/randomness; low entropy means predictable patterns. Natural language typically has entropy between 1-4 bits per character.
What to seek: Lower entropy indicates more predictable text patterns. Entropy should decrease as n-gram size increases.
Coverage (Top-K)
Definition: Percentage of corpus occurrences explained by the top K most frequent n-grams.
Intuition: High coverage with few patterns indicates repetitive/formulaic text; low coverage suggests diverse vocabulary usage.
What to seek: Depends on use case. For language modeling, moderate coverage (40-60% with top-1000) is typical for natural text.
Markov Chain Metrics
Average Entropy
Definition: Mean entropy across all contexts, measuring average uncertainty in next-word prediction.
Intuition: Lower entropy means the model is more confident about what comes next. Context-1 has high entropy (many possible next words); Context-4 has low entropy (few likely continuations).
What to seek: Decreasing entropy with larger context sizes. Very low entropy (<0.1) indicates highly deterministic transitions.
Branching Factor
Definition: Average number of unique next tokens observed for each context.
Intuition: High branching = many possible continuations (flexible but uncertain); low branching = few options (predictable but potentially repetitive).
What to seek: Branching factor should decrease with context size. Values near 1.0 indicate nearly deterministic chains.
Predictability
Definition: Derived metric: (1 - normalized_entropy) × 100%. Indicates how deterministic the model's predictions are.
Intuition: 100% predictability means the next word is always certain; 0% means completely random. Real text falls between these extremes.
What to seek: Higher predictability for text generation quality, but too high (>98%) may produce repetitive output.
Vocabulary & Zipf's Law Metrics
Zipf's Coefficient
Definition: The slope of the log-log plot of word frequency vs. rank. Zipf's law predicts this should be approximately -1.
Intuition: A coefficient near -1 indicates the corpus follows natural language patterns where a few words are very common and most words are rare.
What to seek: Values between -0.8 and -1.2 indicate healthy natural language distribution. Deviations may suggest domain-specific or artificial text.
R² (Coefficient of Determination)
Definition: Measures how well the linear fit explains the frequency-rank relationship. Ranges from 0 to 1.
Intuition: R² near 1.0 means the data closely follows Zipf's law; lower values indicate deviation from expected word frequency patterns.
What to seek: R² > 0.95 is excellent; > 0.99 indicates near-perfect Zipf adherence typical of large natural corpora.
Vocabulary Coverage
Definition: Cumulative percentage of corpus tokens accounted for by the top N words.
Intuition: Shows how concentrated word usage is. If top-100 words cover 50% of text, the corpus relies heavily on common words.
What to seek: Top-100 covering 30-50% is typical. Higher coverage indicates more repetitive text; lower suggests richer vocabulary.
Word Embedding Metrics
Isotropy
Definition: Measures how uniformly distributed vectors are in the embedding space. Computed as the ratio of minimum to maximum singular values.
Intuition: High isotropy (near 1.0) means vectors spread evenly in all directions; low isotropy means vectors cluster in certain directions, reducing expressiveness.
What to seek: Higher isotropy generally indicates better-quality embeddings. Values > 0.1 are reasonable; > 0.3 is good. Lower-dimensional embeddings tend to have higher isotropy.
Average Norm
Definition: Mean magnitude (L2 norm) of word vectors in the embedding space.
Intuition: Indicates the typical "length" of vectors. Consistent norms suggest stable training; high variance may indicate some words are undertrained.
What to seek: Relatively consistent norms across models. The absolute value matters less than consistency (low std deviation).
Cosine Similarity
Definition: Measures angular similarity between vectors, ranging from -1 (opposite) to 1 (identical direction).
Intuition: Words with similar meanings should have high cosine similarity. This is the standard metric for semantic relatedness in embeddings.
What to seek: Semantically related words should score > 0.5; unrelated words should be near 0. Synonyms often score > 0.7.
t-SNE Visualization
Definition: t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding - a dimensionality reduction technique that preserves local structure for visualization.
Intuition: Clusters in t-SNE plots indicate groups of semantically related words. Spread indicates vocabulary diversity; tight clusters suggest semantic coherence.
What to seek: Meaningful clusters (e.g., numbers together, verbs together). Avoid over-interpreting distances - t-SNE preserves local, not global, structure.
General Interpretation Guidelines
- Compare within model families: Metrics are most meaningful when comparing models of the same type (e.g., 8k vs 64k tokenizer).
- Consider trade-offs: Better performance on one metric often comes at the cost of another (e.g., compression vs. OOV rate).
- Context matters: Optimal values depend on downstream tasks. Text generation may prioritize different metrics than classification.
- Corpus influence: All metrics are influenced by corpus characteristics. Wikipedia text differs from social media or literature.
- Language-specific patterns: Morphologically rich languages (like Arabic) may show different optimal ranges than analytic languages.
Visualizations Index
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokenizer Compression | Compression ratios by vocabulary size |
| Tokenizer Fertility | Average token length by vocabulary |
| Tokenizer OOV | Unknown token rates |
| Tokenizer Total Tokens | Total tokens by vocabulary |
| N-gram Perplexity | Perplexity by n-gram size |
| N-gram Entropy | Entropy by n-gram size |
| N-gram Coverage | Top pattern coverage |
| N-gram Unique | Unique n-gram counts |
| Markov Entropy | Entropy by context size |
| Markov Branching | Branching factor by context |
| Markov Contexts | Unique context counts |
| Zipf's Law | Frequency-rank distribution with fit |
| Vocab Frequency | Word frequency distribution |
| Top 20 Words | Most frequent words |
| Vocab Coverage | Cumulative coverage curve |
| Embedding Isotropy | Vector space uniformity |
| Embedding Norms | Vector magnitude distribution |
| Embedding Similarity | Word similarity heatmap |
| Nearest Neighbors | Similar words for key terms |
| t-SNE Words | 2D word embedding visualization |
| t-SNE Sentences | 2D sentence embedding visualization |
| Position Encoding | Encoding method comparison |
| Model Sizes | Storage requirements |
| Performance Dashboard | Comprehensive performance overview |
About This Project
Data Source
Models trained on wikipedia-monthly - a monthly snapshot of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages.
Project
A project by Wikilangs - Open-source NLP models for every Wikipedia language.
Maintainer
Citation
If you use these models in your research, please cite:
@misc{wikilangs2025,
author = {Kamali, Omar},
title = {Wikilangs: Open NLP Models for Wikipedia Languages},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.18073153},
publisher = {Zenodo},
url = {https://huggingface.co/wikilangs}
institution = {Omneity Labs}
}
License
MIT License - Free for academic and commercial use.
Links
- 🌐 Website: wikilangs.org
- 🤗 Models: huggingface.co/wikilangs
- 📊 Data: wikipedia-monthly
- 👤 Author: Omar Kamali
- 🤝 Sponsor: Featherless AI
Generated by Wikilangs Models Pipeline
Report Date: 2026-01-07 00:49:27